We’ve been implementing this ultra-advance SEO for our clients for many years now. Needless to say, the results have never disappointed us (or our clients 🙂).
Table of Content
ToggleBefore we discuss the specifics of the case study, let’s understand how Google understands a piece of content on a website.
Semantic SEO in a nutshell
Google utilizes semantic analysis to understand human language to provide accurate search results. Its understanding of semantically related queries improved with algorithms like Hummingbird and RankBrain.
While traditional lexical search uses direct context keywords, semantic search-based algos are trained to understand patterns and natural language. This means that single keyword-based SEO approaches must be modified to semantic SEO.
It includes building topical depth within the content (using keyword variations) so that the users can get their queries answered within a single piece of content. Semantic content, therefore, helps users get more in-depth information with a single click.
The website
This case study comes from an ecommerce client with a web platform for selling small home items/gifts globally. We worked on the site from 2020 to the beginning of 2022. Our audits showed issues in page optimization, as well as the content.
The content was optimized for primary keywords but failed to consider any relevant LSI (Latent Semantic Index) variations. Additionally, it did not cater well to the search intent and lacked informational depth.
What we did
In addition to our standard SEO techniques (on-page optimization, technical fixes, structured internal linking webs, etc.), we implemented a strategic semantic approach to the site. It included:
- Optimizing for topics, not just keywords.
- Creating subject relevance by developing topical clusters.
- Optimizing the current pages and blogs for keyword clusters (a group of medium-tail keywords with similar semantic relevance) rather than just the primary keyword.
- Creating query-based and intent-based clusters that fall within the same contextual group for Google. (to create a more detailed content network)
- Increasing topical length and depth of blog content to make it more comprehensive (long-form content).
- Including synonyms and keyword variations (semantically-related phrases) that send the right triggers to Google’s NLP algorithms.
- Improving semantic depth of web content by including relevant questions.
- Using structured data (schema) to add context to the content.
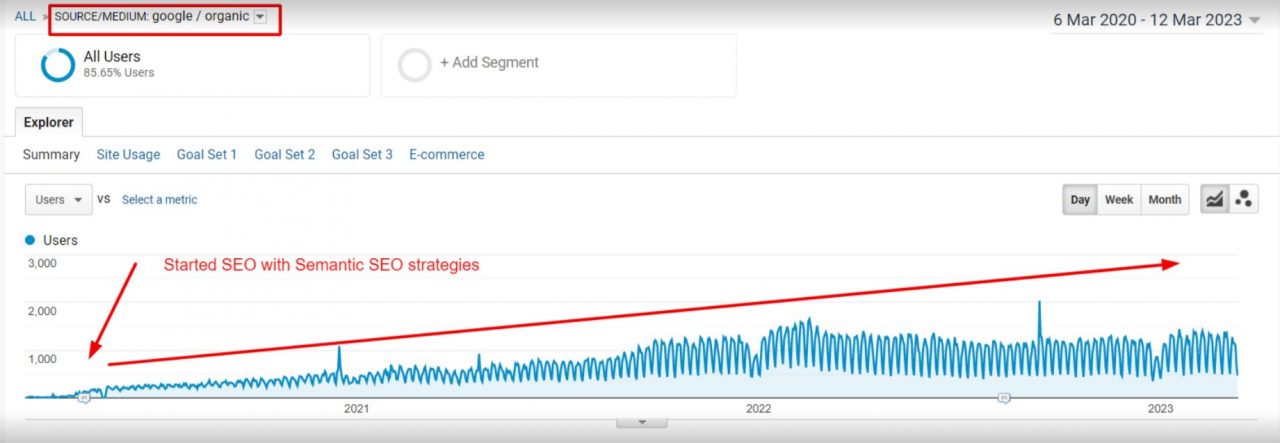
Results
- Organic users increased by about 1400% (between 2020 to beginning of 2022).
- While at the start of 2020, the website ranked for only a few hundred keywords, it was ranking for approximately 11,000 keywords in the beginning of 2022.
- The website is now ranked on page 1 for many competitive keywords related to their most important speciality products.
- Some of the newly ranked medium tail keywords with high transactional intent are now being ranked in the top 10, bringing them higher conversion rates and revenues.
Semantic SEO depends on deducing meaning out of topics, words, or concepts. There are a host of other strategies in this context to help web content get more love from the semantic search engines we have today.
We’ll talk more about these in our future case studies.
For more case studies, visit us at https://www.growth.pro/seo-case-study.
